Services
- taxlot-specific zoning data
- cartography for zoning and project plans
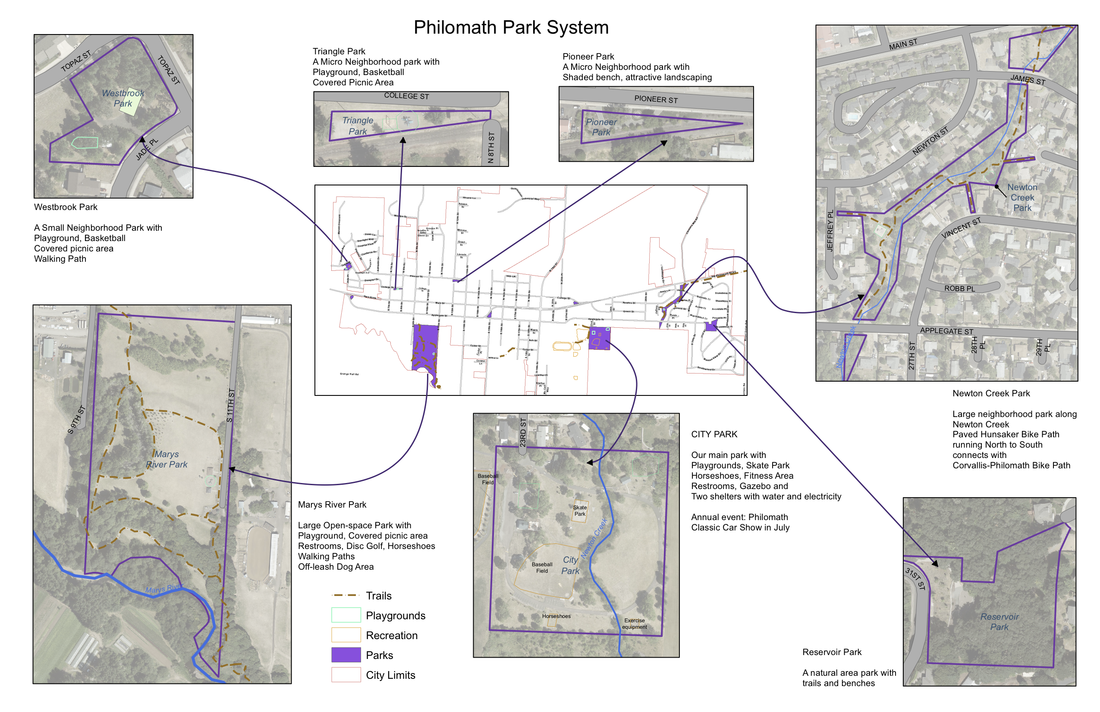
- park system maps
- comprehensive plan maps
- natural hazards: flood zone overlay; landslide risk
Why do we need GIS in urban planning?
|
Development does not happen in a vacuum and GIS is the perfect tool to help planners discover potential issues arising from the use of natural and urban space so the best decision can be made very quickly.
|
Current Land Use records contain vital information for all city management personnel and can be easily accessed via GIS.
|
|
Zoning and property-specific information is best organized and linked together using GIS. GIS will save you many hours searching for and gathering information from many different sources.
|
Updates or changes to a comprehensive plan can be quickly analyzed to aid in decision making.
|
Keep GISCNR on your radar!
Sections below provide a brief illustration of how GIS can be
essential for planners and city administrators.
essential for planners and city administrators.
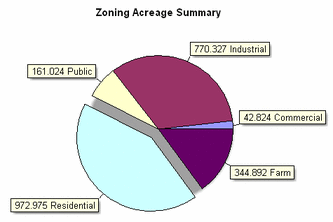
ZoningMapping both current land use and future zoning helps decision makers visualize how a community will change over time. GIS also facilitates quantitative analysis of how much land is dedicated for particular purposes. Using a pie chart, easily created from a GIS data table, is just one useful spatial analysis tool among many.
Zoning is related to nearly everything that happens in a community from parks and natural resources to State mandates and Capital Improvement Districts.
Natural Resources
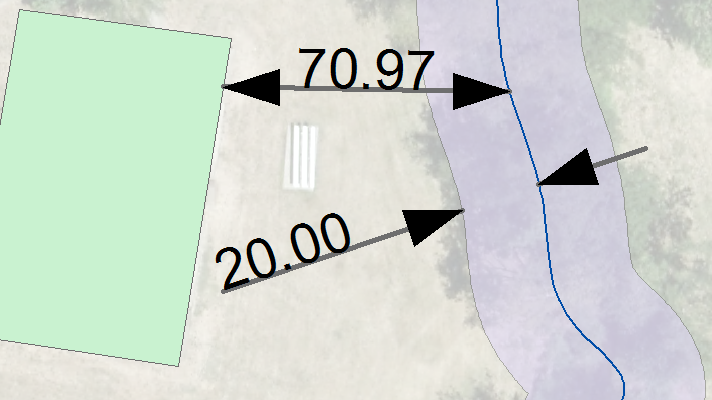
Many communities struggle to include natural resources in planning considerations because measurements and modeling are time consuming. GIS helps to determine the spatial relationship between development and natural areas. The clip below shows that the riparian stream buffer is 20 feet wide from center stream to edge of designated riparian space and the structure is nearly 80 feet from the stream.
|
Impervious Surfaces
Using digital visualization and measurement, assessment of the impacts of impervious surfaces is simplified with GIS.
Impervious surfaces (also know as hardscapes) impact water quality in natural streams by increasing stormwater runoff. Runoff contains many contaminants and warms natural streams which negatively affects aquatic life. Knowing how much impervious surface will be created by particular activities is a tool to help determine SDC's, to guide development type and scale, and impervious surfaces may (or may not) contribute to successful application for flood insurance rate reductions for residents in Special Flood Hazard Areas. Impervious surfaces can be accurately measured to ensure that the City recovers the appropriate costs related to the impacts of hardscapes. Parks
Park planning involves many topics including the spatial distribution and acreage of park systems compared to the populations they serve.
Through visualization and measurement, GIS facilitates park planning to ensure that all of the City's population has adequate access to open spaces. Visualization
Visualization is invaluable in places where paper documentation is either extensive (too much to process quickly) or missing (non-existent). The benefits of using GIS to visualize alternative configurations and the impacts of visualization on decision making cannot be overstated.
It just works! |